

Very often permutations are mistaken for combinations, at least in common language use. For example, if you are thinking of the number of combinations that open a safe or a briefcase, then these are in fact permutations, since changing the order of the numbers or letters would result in an invalid code. Permutations are for ordered lists, while combinations are for unordered groups. With combinations we do not care about the order of the things resulting in fewer combinations. The difference between combinations and permutations is that permutations have stricter requirements - the order of the elements matters, thus for the same number of things to be selected from a set, the number of possible permutations is always greater than or equal to the number of possible ways to combine them. 6 = 36 possible permutations of the two dice rolls.The answer in this case is simply 6 to the power of 2, 6 double sixes) it is a calculation of permutation with repetition. This a case of randomly drawing two numbers out of a set of six, and since the two may end up being the same (e.g. If two six-sided dice are thrown together, one needs to estimate the number of possible ways they may come up. The formula for calculating the number of possible permutations is provided above, but in general it is more convenient to just flip the "with repetition" checkbox in our permutation calculator and let it do the heavy lifting.Īnother common example concerns dice probabilities.
#8 PERMUTE 2 CODE#
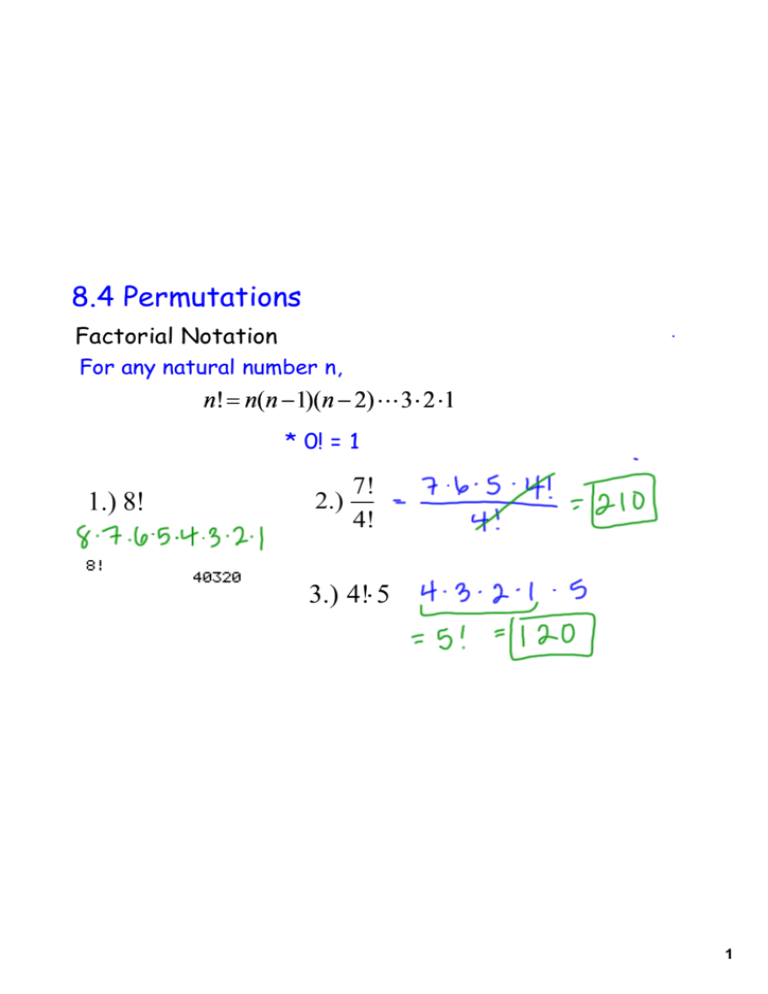
Or you can have a PIN code that has the same number in more than one position. you can have a lock that opens with 1221. For example, locks allow you to pick the same number for more than one position, e.g. In some cases, repetition of the same element is allowed in the permutation. For example, a factorial of 4 is 4! = 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 24. In both formulas "!" denotes the factorial operation: multiplying the sequence of integers from 1 up to that number. If the elements can repeat in the permutation, the formula is:

The above equation can be said to express the number of ways for picking r unique ordered outcomes from n possibilities. To calculate the number of possible permutations of r non-repeating elements from a set of n types of elements, the formula is:
Permutation calculations are important in statistics, decision-making algorithms, and others. The possible permutations would look like so: Say you have to choose two out of three activities: cycling, baseball and tennis, and you need to also decide on the order in which you will perform them. Here is a more visual example of how permutations work. A given phone area prefix can only fit in that many numbers, the IPv4 space can only accommodate that many network nodes with unique public IPs, and an IBAN system can only accommodate that many unique bank accounts. are designed based on the knowledge of the maximum available permutations versus the expected use. Systems like phone numbers, IP addresses, IBANs, etc. Permutations come a lot when you have a finite selection from a large set and when you need to arrange things in particular order, for example arranging books, trophies, etc.Ĭalculating permutations is necessary in telecommunication and computer networks, security, statistical analysis. For example, if you have just been invited to the Oscars and you have only 2 tickets for friends and family to bring with you, and you have 10 people to choose from, and it matters who is to your left and who is to your right, then there are exactly 90 possible solutions to choose from. A permutation is a way to select a part of a collection, or a set of things in which the order matters and it is exactly these cases in which our permutation calculator can help you.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
