
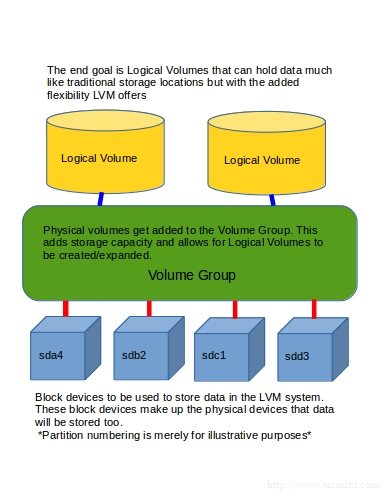
To scan the block devices to be used as PVs, use the lvmdiskscan command. Before creating the PV, make sure the disk is visible in the OS. The pvcreate command is used to initialize the PV for use by LVM. Create a File system on this LV and mount it ( /data01). Create a Lgical Volume in this VG ( /dev/vg01/lvol01).Ĥ. Create Volume group from these 3 PVs ( /dev/vg01).ģ. Create 3 Physical volumes from 3 physical disks ( /dev/sdb, /dev/sdc, /dev/sdd).Ģ. Once the file system is created we can mount the logical volume as per our need. The command mkfs can be used to create file system on top of a logical volume. File systemįile systems are built on top of logical volumes. You can use command lvcreate to create a logical volume in an existing volume group. Logical volumes are block devices which are created from the physical extents present in the same volume group. Logical Volume (LV)Ī Logical Volume is the conceptual equivalent of a disk partition in a non-LVM system. – Generally, larger the PE size, better the performance (though less granular control of LV). – The default size of PE is 4MB, but you can change it to the value you want at the time of VG creation. The size of PE can differe in different VGs and is defined at the time of creating VG. – VGs are made up of PVs, which in turn are made up of physical extents (PEs). The command vgcreate creates a new volume group using the block special device Physical Volume path previously configured for LVM with pvcreate. Volume group is divided into fixed size physical extents. Volume Group (VG)Ī Volume Group gathers together a collection of Logical Volumes and Physical Volumes into one administrative unit.

Initializing a block device as physical volume places a label at the start of the device. Use the command pvcreate to initialize storage for use by LVM. While a copy is being made, any new information that needs to be added to the logical volume is written to the disk just like normal, but changes are tracked so that the original picture never gets destroyed.The conceptual layers are in turn made up of smaller units like Physical extents(in case of Physical volumes) and Logical extents (in case of Logical Volumes).Įach Physical Volume can be a disk partition, whole disk, meta-device, or a loopback file. When LVM takes a snapshot, a picture is taken of exactly how the logical volume looks and that picture can be used to make a copy on a different hard drive. LEs are abstract chunks of storage mapped by the LVM to Physical Extents in a volume.
LOGICAL VOLUME MANAGER LINUX OFFLINE
One of the coolest things about LVM snapshots is your file system is never taken offline and you can have as many as you want without taking up extra hard drive space. Logical Volumes are virtual disk devices made up of Logical Extents (LEs). Snapshots is a feature that some newer advanced file systems come with but ext3/4 lacks the ability to do snapshots on the fly. RELATED: Which Type of RAID Should You Use For Your Servers? Backing up a Logical Volume


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
